
The WHD concluded that the annual bonus program required recalculation. The WHD concluded that the quarterly bonus, but not the annual bonus, complied with the FLSA’s overtime requirements. The opinion letter involves two types of nondiscretionary bonuses: (1) an annual bonus, which equals “1 percent of the journey straight-time hourly rate for 2,080 hours” and (2) a quarterly bonus consisting of multiple parts: (a) 15 percent of the employee’s contractual straight-time hourly rate for each hour a straight-time rate is earned, (b) 22.5 percent (1.5 × 15 percent) of the employee’s contractual straight-time hourly rate for each hour an overtime rate is earned, and (c) 18.75 percent (1.25 × 15 percent) of the employee’s contractual straight-time hourly rate for each hour earned at a double-time rate. The WHD Opinion Letter Applies the General Rules
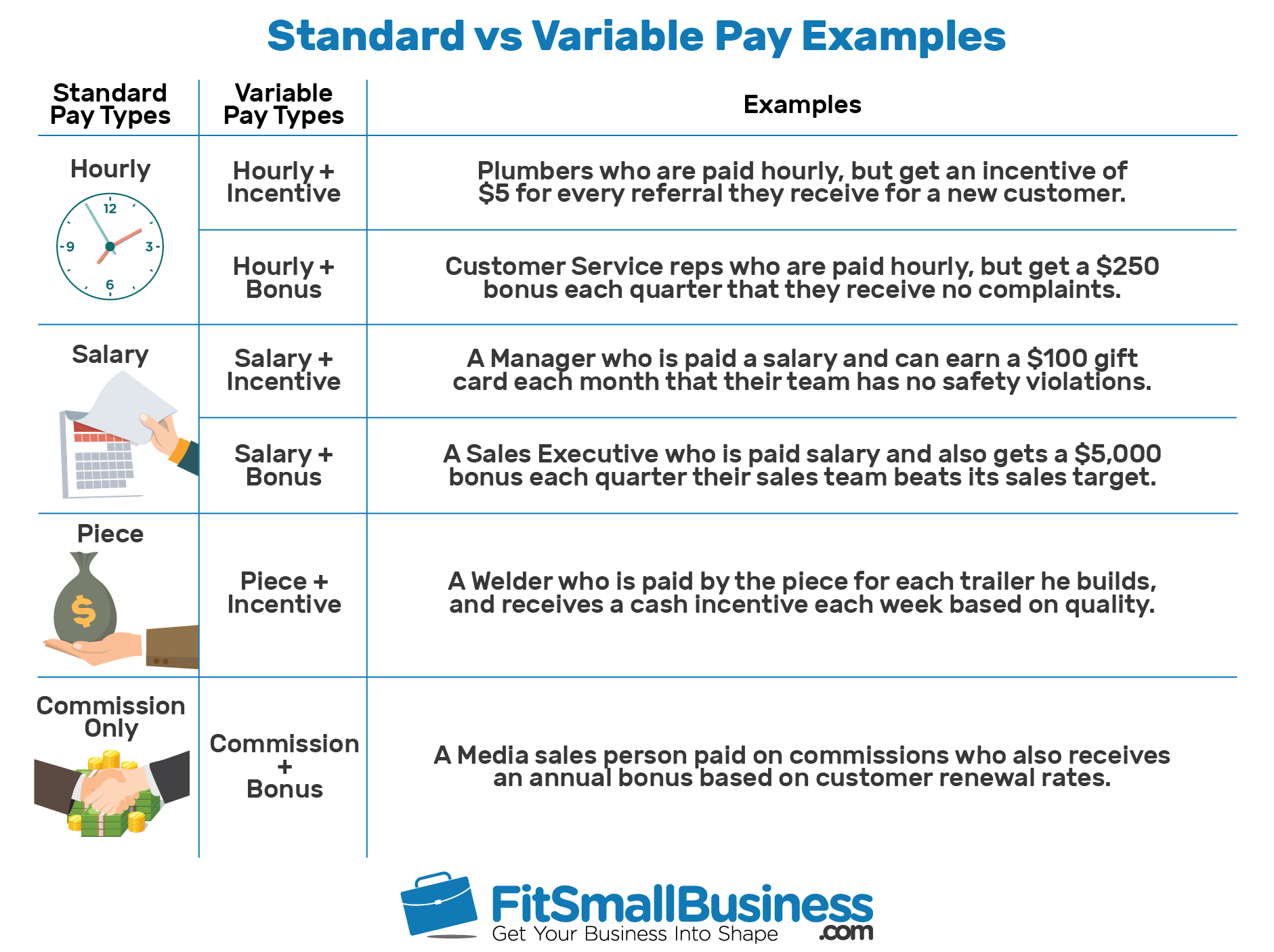
The opinion letter explains this recalculation process and also highlights certain bonus structures that do not require recalculation because the bonus plan “simultaneously pays overtime compensation due on the bonus.” This often requires the employer to recalculate an employee’s regular rate of pay once the bonus is earned and payable, and then pay the employee an increased overtime premium due on the bonus. Because most nondiscretionary bonuses are included in the regular rate of pay, the FLSA might require an employer to pay an overtime premium on a nondiscretionary bonus depending on how the bonus is earned under the employer’s bonus plan. The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) defines “regular rate of pay” to include “all remuneration for employment paid to, or on behalf of, the employee” and the term “remuneration” generally includes nondiscretionary bonuses. General Rules Regarding Nondiscretionary Bonuses

Department of Labor’s Wage and Hour Division (WHD) issued Opinion Letter FLSA2019-7, which discusses how employers may account for overtime pay as part of annual and quarterly nondiscretionary bonuses.
#BONUS OVERTIME CALCULATION EXAMPLES HOW TO#
A common challenge for employers of hourly or nonexempt employees who receive quarterly or annual nondiscretionary bonuses is how to factor such bonuses into the employees’ regular rates of pay and calculate the appropriate overtime premiums due to those employees who work more than 40 hours in a workweek.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
